VMware Workstation is a virtual machine to run operating systems installed on a computer. A VMware virtual machine emulates computer hardware, allows you to create virtual machines, run one or more operating systems that run in parallel with the Windows installed on the computer.
VMware Workstation Pro emulates the hardware of a computer and allows you to run software on a computer in an isolated environment. On a virtual machine, you can install operating systems (for example, Linux on Windows, or vice versa) to work in a virtual environment without affecting the real system.
Content:
- Create a new virtual machine
- Configure VMware Virtual Machine
- Opening a virtual machine
- Running Guest OS on VMware Workstation
- Install VMware Tools
- Guest OS Snapshots
- Disabling a virtual machine
- How to enter the BIOS of a VMware virtual machine
- Removing a virtual machine
- Conclusions of the article
Check unfamiliar or suspicious software, check a new antivirus in operation, without installing it on your computer, try to work in another operating system, etc. At the same time, the real operating system will not be affected in case of dangerous actions performed on the virtual machine.
The actual operating system installed on the computer is called the host, and the operating system installed on the virtual machine is called the guest operating system.
The American company Vmware, the largest manufacturer of virtualization software, produces programs for personal computers: paid VMware Workstation Pro and free VMware Player with reduced capabilities.
VMware Workstation Pro (in the article an overview of this program) supports the installation of several different (or the same) operating systems: various distributions of Windows, Linux, BSD, etc.
Please note that the guest operating system consumes computer resources. Therefore, while the virtual machine is running, you should not run resource-intensive applications on a real computer, and also open several virtual machines at once. The more powerful the computer, the more comfortable it is in a virtual machine. On powerful computers, several virtual machines will work simultaneously without problems, and on weak computers, only one virtual machine.
Install VMware Workstation Pro on your computer. By default, the program runs in English, on the Internet there is a good Russification from Loginvovchyk, which must be installed after installing the program. After that, the VMware Workstation Pro virtual machine will work in Russian.
After starting, the main VMware Workstation window opens. At the top of the window is a menu for managing the program. On the left is the "Library", which displays the virtual machines installed in VMware. The “Home” tab contains buttons for performing the most frequently requested actions: “Create a new virtual machine”, “Open a virtual machine”, “Connect to a remote server”, “Connect to Vmware vCloud Air”.
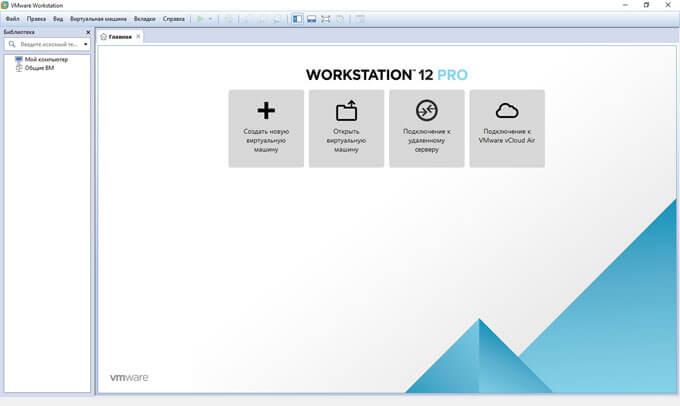
Create a new virtual machine
To create a virtual machine (VM), click on the "Create a new virtual machine" button, or go to the "File" menu, select "New virtual machine ...".
The Create New Virtual Machine Wizard opens. In the first window, select the configuration type "Normal (recommended), and then click on the" Next "button.
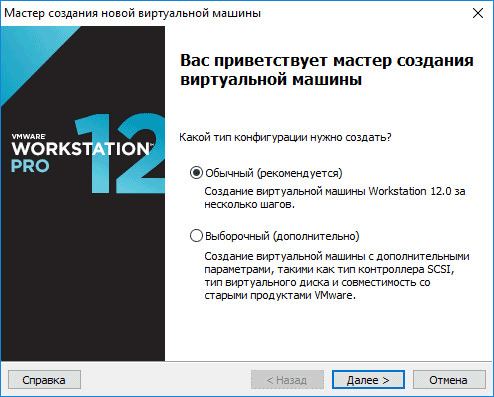
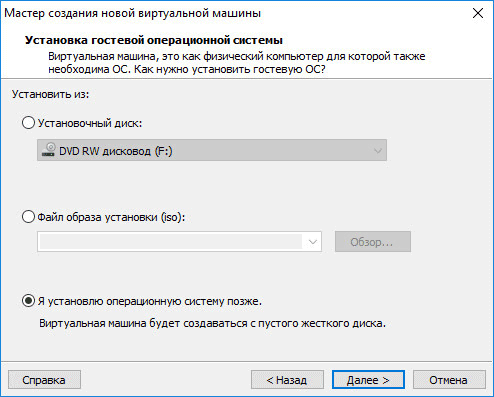
The next window offers a choice of the type of guest OS installation; three options are available:
- installation from the installation DVD disc inserted in the computer’s drive;
- use to install the system image file in ISO format from a computer;
- installing the operating system later.
If you select the first two options, after selecting the settings, installation of the operating system on the virtual machine will begin. In the third case, the installation of the guest OS can be started at any other convenient time, after the configuration of the virtual machine is completed.
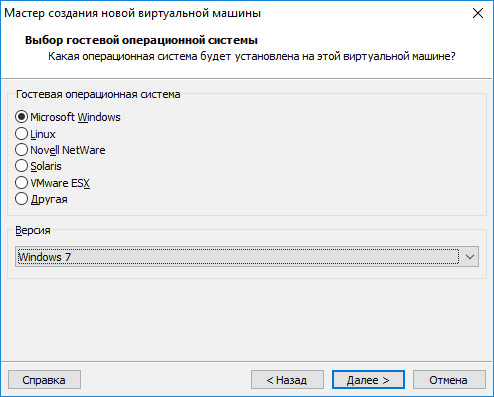
If installing later, select the guest operating system. If it is not in the list, select “Other”. Then select the OS version. A large selection of versions for each system is offered (in total, more than 200 OSs are supported), there is also the Other option of various bit sizes (34-bit and 64-bit).
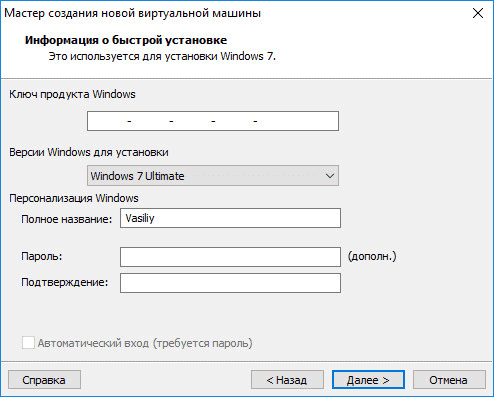
If you install the guest system in the process of creating a virtual machine, then a window with information about quick installation will open. Windows product key and password are optional; enter only the Windows version.
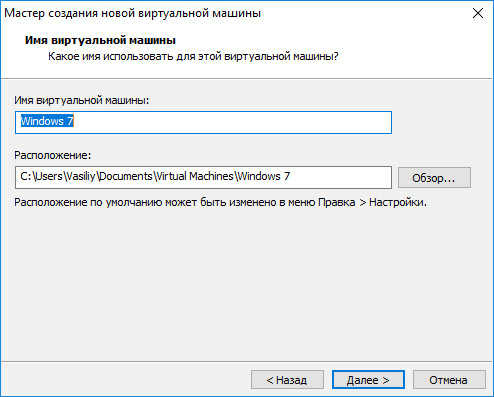
Next, you will need to select the name of the virtual machine and the location of the virtual machine. Give a friendly name to the virtual machine and select a path for its location.
If your computer has more than one logical drive, then I recommend changing the location of the storage location of the virtual machine files in the user profile (default setting) to another drive on your computer.
What is it for? In the event of a Windows failure installed on the computer, a system reinstall will be required. After reinstalling the operating system, the VMware virtual machine file saved in the user profile on the system drive will be lost. If the virtual machine is not located on the system drive, then reinstalling Windows will not affect it.
For reuse, you will need to install VMware Workstation, and then connect the virtual machine. You do not have to reinstall and configure everything.
Therefore, on disk “E” (in your case, most likely there will be disk “D”) on my computer, I created a folder called “Virtual Machines”, in which folders with files of virtual machines installed on my computer are saved.
For a new virtual machine, create a folder with the name of this VM in order to separate its files from other VMs.
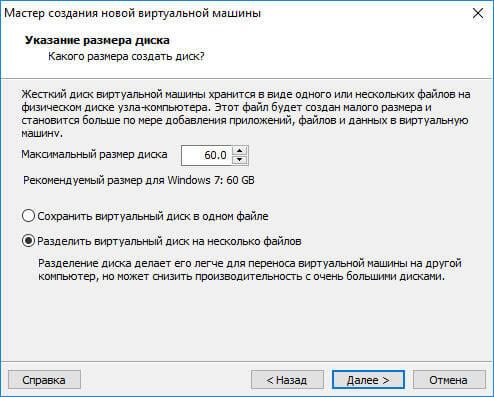
Next, you need to select the maximum size of the disk occupied by the virtual machine (by default - 60 GB, the size can be changed), the type of storage of the virtual disk: in one file, or in several files. This size will be taken from the hard drive of your computer for the needs of the virtual machine.
When saving a virtual disk in one file, the VM works more efficiently than when splitting into several files.
Accept the recommended settings, or choose a more suitable option for your computer.
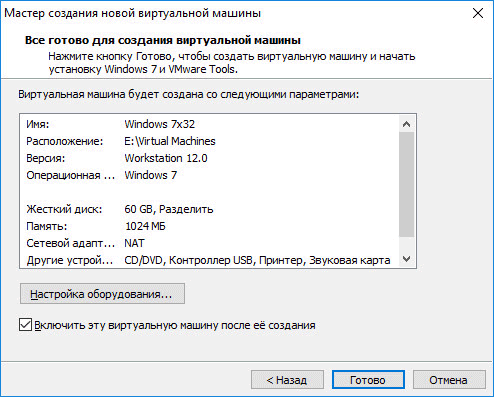
In the final window, click on the "Finish" button. After that, the installation of the guest operating system will begin.
Read more about the Windows installation process in the articles on my site.
If you selected the setting for installing the operating system later, then this window will not have the option “Enable this virtual machine after its creation”, and accordingly the installation of the guest system will not start.
Configure VMware Virtual Machine
By default, the virtual machine is configured optimally for most cases. If necessary, you can change some parameters, as well as add shared folders.
In the settings, in the "Hardware" tab, you can change the amount of memory for this virtual machine, the number of processor cores, and the amount of hard disk occupied by the virtual machine. In the "CD / DVD (SATA)" section, you can select the drive or image file of the operating system to install (if you select the installation later), make other settings.
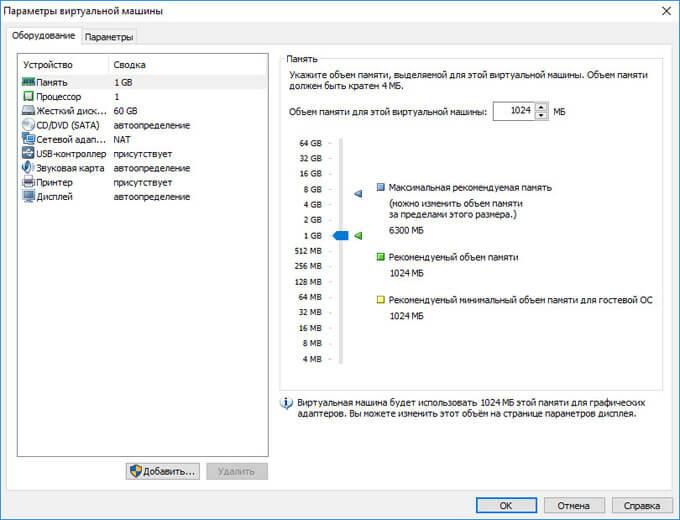
In the "Settings" tab, in the "Shared Folders" section, select the "Always On" setting, activate the "Connect as a network drive in Windows guest" option.
Next, click on the "Add ..." button, in the Add Shared Folders Wizard window, create a shared folder for exchanging data with the real system and other guest systems. It is desirable to create a shared folder not on the system drive for the reasons described above.
There is already such a folder (Data Sharing) on my computer. I selected this folder for the new virtual machine. Next, enable this resource.
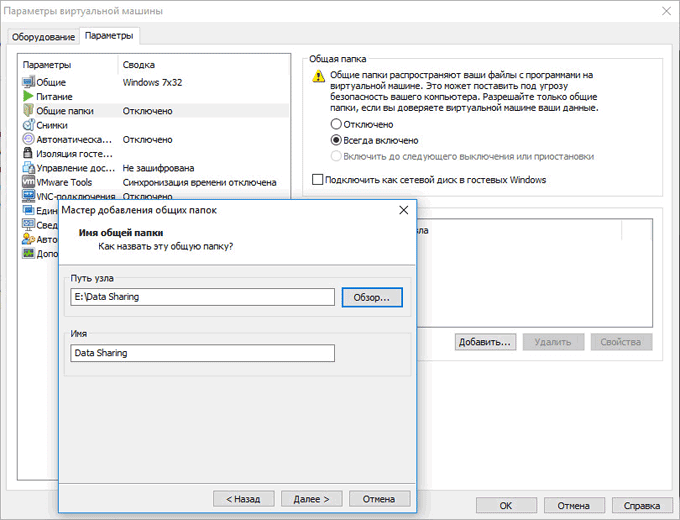
With the default settings, drag and drop, paste and copy files from the real to the virtual system are allowed, and in the opposite direction.
Opening a virtual machine
After reinstalling Windows (my case), you can open previously created virtual machines stored on your computer. In the main window of VMware Workstation, click on the "Open Virtual Machine" button, or in the "File" menu, select "Open ...".
Select the file (on my computer the virtual machines are located in the “Virtual Machines” folder) of the virtual machine, and then click on the “Open” button.
On my computer, I opened previously saved virtual operating systems: Windows 10 x64, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Mac OS X.
Running Guest OS on VMware Workstation
To start the guest operating system, in the VMware Workstation Pro program window, select the tab with the desired OS (if several guest OSs are installed), and then click on the “Enable Virtual Machine” button. You can turn on the system from the menu “Virtual Machine”, “Power”, “Start Virtual Machine”.
Next, the guest virtual OS window opens, which can be opened on the entire monitor screen.
To release the mouse cursor from the virtual machine, press the keys “Ctrl” + “Alt”, and to switch the mouse cursor to the virtual machine “Ctrl” + “G” (or click in the window of the virtual machine).
Install VMware Tools
VMware Tools - a package of drivers and services that improve the virtual machine and its interaction with peripheral devices. Immediately after installing the operating system on the virtual machine, you need to install VMware Tools. A reminder will appear in the program window.
In the "Virtual Machine" menu, select "Install VMware Tools ...". Next, open Explorer, start the installation of VMware Tools from the CD-ROM drive. After completing the installation of the package, restart the guest operating system.
Guest OS Snapshots
In VMware Workstation, you can take a snapshot of the state of the guest OS. After creating a snapshot of the state of the system, in case of failures in the guest OS, you can return to the previous working state of the system.
In the menu "Virtual machine" you need to click on the item "Create a snapshot." Next, give a name to the picture, if necessary, add a description.
To restore the state of the guest OS at the time of creating the snapshot, select "Return to Snapshot: Snapshot N" in the context menu. Next, restore the system state. The current state of the OS will be lost.
Created snapshots can be managed through the Snapshot Manager: create, clone, delete snapshots. The menu bar has three buttons for managing snapshots of the system.
Disabling a virtual machine
To exit the virtual machine, in the "Virtual Machine" menu, click on the "Power" item in the context menu, and then select "Shut down the guest OS". The operating system will shut down as if the computer was shutting down normally.
When you select the "Suspend guest OS", the system will suspend its work, without disabling services and applications.
How to enter the BIOS of a VMware virtual machine
In the process of starting the virtual machine, it is not possible to enter the BIOS due to the fact that the BIOS screen loads almost instantly.
In order for the user to be able to enter the BIOS of the virtual machine when the system boots, you must open the configuration file (.vmx file extension) of the virtual machine in Notepad. The configuration file is located in the virtual machine folder, in the location selected when creating the virtual machine.
Enter the following line at the very end of the configuration file:
bios.bootdelay = 15000
This parameter sets the BIOS screen delay in milliseconds, in this case, 15000 = 15 seconds. You can choose a different time interval.
Now the user will be able to press the desired key on the BIOS screen that appears.
Removing a virtual machine
To remove a virtual machine, open the tab for that virtual machine in VMware Workstation Pro. In the "Virtual Machine" menu, select the "Manage" item in the context menu and then the "Delete from disk" item. In the warning window, agree to delete (this is an irreversible action).
After that, all files of the guest virtual machine will be deleted from the computer.
Conclusions of the article
VMware Workstation Pro virtual machine is a powerful application for creating guest virtual operating systems running on a computer, along with a real OS. The guest operating system will be isolated from Windows installed on the computer.